An array is a list of values of the same type. Arrays allow programmers to access multiple values using one identifier.
(Image from javatutorial.net)
Example problem
Consider this problem:
Given 6 words, output them in reverse order.
For example, if the input is:
I really enjoy doing ICS homework
then the output should be:
homework ICS doing enjoy really I
Without an array
Without using an array, this is what the program could look like:
public static void revInputNoArray() {
String w1, w2, w3, w4, w5, w6;
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
w1 = input.next();
w2 = input.next();
w3 = input.next();
w4 = input.next();
w5 = input.next();
w6 = input.next();
System.out.println(w6 + ' ' + w5 + ' ' + w4 + ' ' + w3 + ' ' + w2 + ' ' + w1);
}
Clearly, this is tedious to write, and the code is very repetitive. If there were 1000000 words instead of 6 words, then this would take nearly forever to code.
With an array
Let’s see how we can improve this by using an array:
public static void revInputWithArray() {
String[] words = new String[6];
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
for (int i = 0; i < 6; ++i) {
words[i] = input.next();
}
for (int i = 5; i >= 0; --i) {
System.out.print(words[i] + ' ');
}
System.out.println();
}
The code above looks much less repetitive. words is an array of 6 Strings, which can be iterated over using a for loop.
Java arrays are declared with the syntax Type[] identifier and created using the syntax new Type[length].
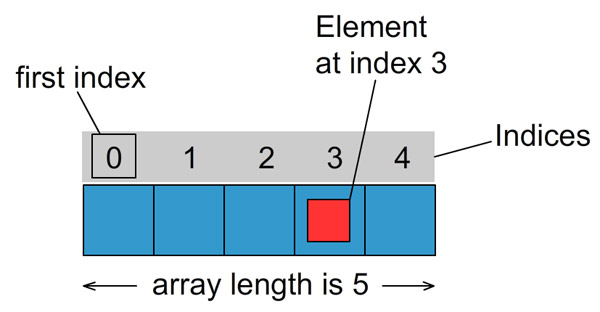
To access an element in an array, you put the element’s index within square brackets. Java arrays are zero-indexed, meaning that the indexes start from zero and go up to the length of the array minus one. The first element is at index 0, the second is element is at index 1, the third element is at index 2, and so on.
Other syntax
Specifying initial elements
Another way to create an array is by listing its initial elements. The code below creates an array named phrases which contains 3 Strings, and initializes the Strings.
String[] phrases={"hello", "goodbye", "good morning"};
Getting the length of an array
To get the length of an array, use its length property:
System.out.println(phrases.length); // should print "3"
Foreach loop
To loop over the elements of an array, you can use a for loop:
for (int i = 0; i < phrases.length; ++i) {
System.out.println(phrases[i]);
}
Alternatively, if you need to iterate over the elements, but don’t need to assign values to them, you can use the more concise foreach loop:
for (String phrase : phrases) {
System.out.println(phrase);
}
The foreach loop eliminates the need for a counter variable; you just specify a name for the variable used to access each element (phrase in this example).
Conclusion
Arrays are an essential part of Java; without them, you wouldn’t be able to efficiently work with large amounts of data. Hopefully this tutorial helped familiarize you with Java arrays. The next tutorial will cover the ArrayList data structure, which is similar to an array, except it can be resized dynamically.